All About Cotton: Exploring Nature’s Versatile Fiber
Cotton is a most widely used natural fiber, and also plays a crucial role in the textile industry. In the years 2022 and 2023, the world produced around 118.3 million bales of cotton. The leading producers were India, China, and the United States, contributing to over half of the global production. By 2022, the total global cotton supply, including stocks, reached approximately 241.15 million bales. (From Statista)
With just a few numbers, you can already see the significant impact of cotton, right? However, that’s not all, and you will learn a lot more about cotton through this article.

What is Cotton?
Cotton fibers are sourced from cotton plants, obviously. More specifically, they originate from the outer layer of the seeds of these plants. To make sheets or t-shirts, the cotton seeds need to be separated from the plant, and then the fibers are extracted from the seeds.
History of Cotton Fabric
Cotton’s history dates back to ancient times. Scientists have found evidence of cotton bolls and cloth that are at least 7,000 years old in caves in Mexico, which closely resemble the cotton grown in America today. In the Indus River Valley in Pakistan, cotton was being grown, spun, and woven into cloth as early as 3,000 years BC. Similarly, the natives of Egypt’s Nile valley were making and wearing cotton clothing around the same time.
Cotton cultivation in America began with the planting of cotton seeds in Florida in 1556 and Virginia in 1607. By 1616, colonists were growing cotton along the James River in Virginia. The industrial revolution in England and the invention of the cotton gin in the U.S. paved the way for cotton’s prominence in the world. Eli Whitney’s patent for the cotton gin in 1793 revolutionized cotton production, making it ten times faster than manual labor.

The combination of textile mills and cotton gins in America led to the rapid growth of the cotton industry. By the 1860s, America was producing 2/3 of the world’s cotton, earning the phrase “Cotton is King” to describe the American economy’s growth. However, the dark side of this growth was the exploitation of slave labor, which still has repercussions in some cotton plantations today.
Cotton continues to be the most widely used textile worldwide, finding its way into clothing, home textiles, bed linen, and hygiene products. The quality of cotton varies, with Egyptian cotton and Pima cotton known for their luxurious softness and staple length.
From Raw Cotton to Cotton Fabric
Here is a simplified description of the production process of cotton, which gives you a glimpse of the entire process of fabricating cotton textiles.
What is Cotton Fabric Used For?
Approximately 75 percent of the world’s clothing products contain at least some amount of cotton. In sheer numbers, cotton is the most widely used textile fiber in the world, and manufacturers can spin this fabric into a myriad of different types of products.
It is commonly used to make clothing like t-shirts, jeans, and dresses because it is comfortable and breathable. You can also find cotton fabric in bed sheets, towels, and curtains because it is soft and absorbent. Cotton is even used to make bags, shoes, and upholstery for furniture. Its versatility and durability make it a popular choice for a wide range of products.

Types of Cotton Fabrics
There are approximately 43 different types of cotton fabrics worldwide, categorized into four main groups:
- Gossypium hirsutum: Cotton grown in highland regions of Central America, Mexico, and the Caribbean, accounting for about 90% of global production.
- Gossypium barbadense: This variety has longer cotton fibers and is cultivated in South America, representing 8% of total global production.
- Gossypium arboreum: Grown in India and Pakistan, accounting for 2% of total production.
- Gossypium herbaceum: Cultivated in South Africa and the Arab region, making up 2% of total production.
Quality Assessment Standards for Cotton Fabrics

Generally, longer cotton fibers tend to produce higher-quality fabric due to their ability to withstand more processing steps, resulting in smoother finished products and a better tactile experience.
- The length of cotton fibers ranges from 3.2 to 63.5mm.
- The standard length for production ranges from 22.2 to 31.5mm.
3 Most High-Quality Cotton Fabrics

There are 3 types of fabrics with the best quality and most used all over the world:
- Egyptian Cotton (fiber length of 36-44mm): The best quality cotton is the Barbadense variety, which has longer fibers. Combined with the climate and geography of its origin, Egyptian Cotton is considered luxurious, refined, and superior.
- Sea Island Cotton (fiber length of 35-64mm): This type of cotton has natural fungus resistance, making it naturally resistant to insects and diseases.
- Pima Cotton (fiber length of 35-41mm): Similar to Barbadense, Pima Cotton is mainly grown in Arizona, New Mexico, southwestern Texas, and parts of southern California, where the climate is very dry and hot. Supima Cotton, a type of Pima Cotton, is scarce and therefore expensive.
The Negative Impact Of Cotton Fabric On The World
We already know the reasons why cotton fabric is so popular and used so much. So now it’s time to learn about its downside.
Why is cotton called the dirtiest crop in the world?
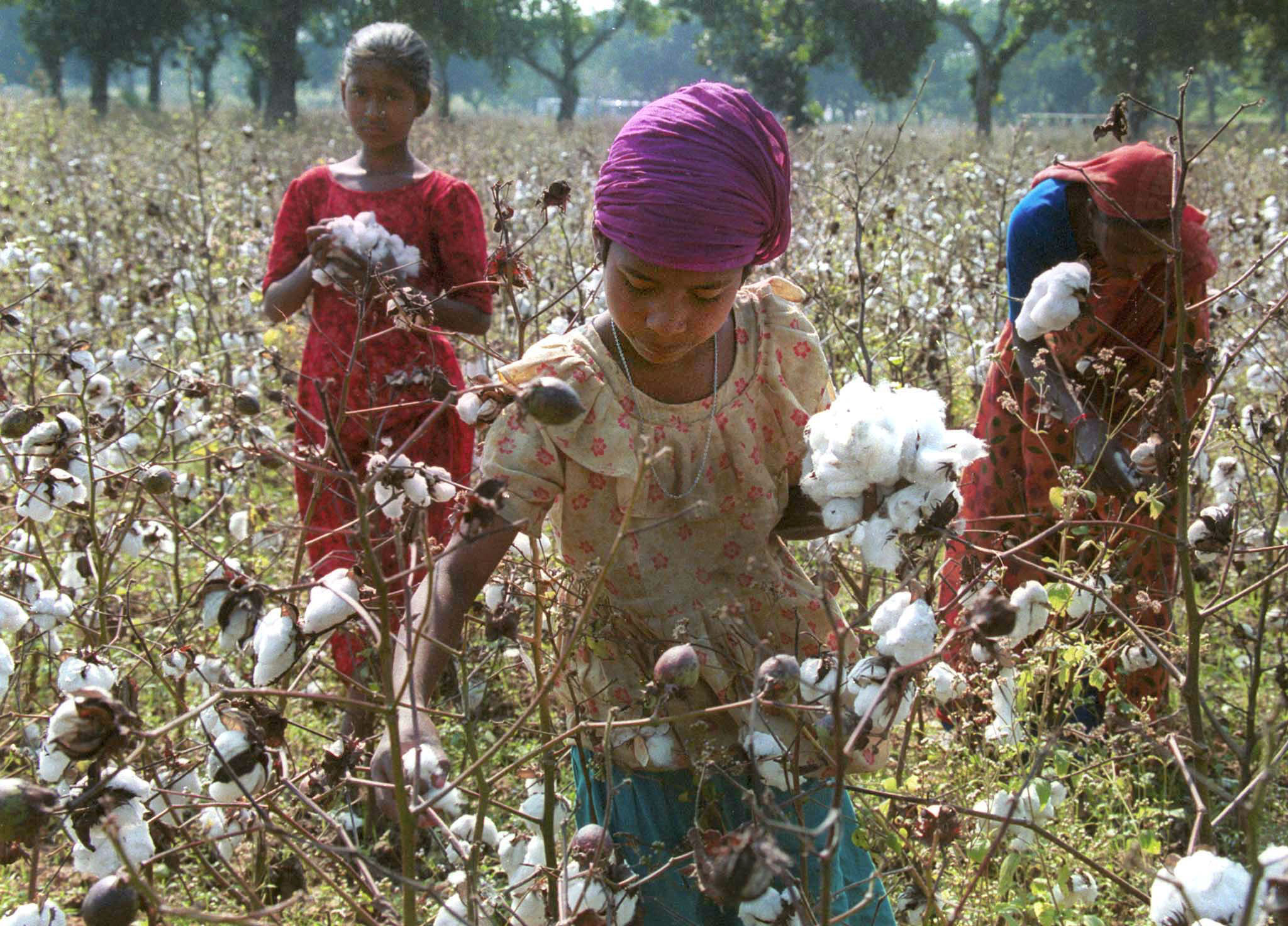

In essence, cotton production itself does not have a significant impact on the environment. As this fabric is made from natural fibers, it has the ability to biodegrade and does not contribute to waterway congestion or other forms of pollution.
However, the environmental harm primarily stems from the methods used by manufacturers in cotton production. Cotton cultivation requires a substantial amount of water, and the manufacturing process can also be linked to land degradation.
Since most cotton producers focus on maximizing fiber yield at the lowest cost, they may not properly care for the land used for cultivation. As a result, cotton cultivation often leads to land depletion in those regions.
Additionally, cotton is a crop that heavily relies on pesticides. It is grown on only 2.5% of the world’s agricultural land but consumes 16% of total pesticide use and 7% of total herbicide use worldwide—more than any other crop. Highly toxic chemicals, including nerve agents and carcinogens, are used on cotton plants.
Ethical Issues in Cotton Production
In most cases, cotton cultivation involves exploitative practices where international corporations take advantage of impoverished and uneducated individuals in third-world countries to produce these fibers. The use of cheap labor is prevalent, and even some countries, such as China, have faced global condemnation for employing child labor in cotton production.
Child labor is directly involved in pesticide spraying on cotton plants, often without any protection. Due to their smaller body size, different metabolic processes, and rapidly developing organ systems, children are much more vulnerable to the negative impacts of pesticide exposure and are at greater risk of harm.
Certification of Cotton Fabrics

In reality, there are various certifications available for cotton manufacturers. For example, the European Union’s organic standard organization can certify cotton as organic, and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) can do the same.
Another company called OEKO-TEX certifies organic textile products. Additionally, all Supima cotton is organic, and the Supima Association of the United States (ASA) must certify Pima cotton to be considered Supima.
|
And that is also the criteria for selecting fabric suppliers for K-Embroidery. In order to produce highly regarded smocked children’s clothing as we do today, we have to choose cotton fabric suppliers with the aforementioned certifications. Although this may result in higher import costs for us, we still prioritize sustainability and product quality. |
Conclusion
In summary, cotton is an excellent fabric for producing clothing because it is breathable, highly absorbent, and cost-effective. It is great to wear in both warm and cool weather. However, clothing manufacturers should also choose fabric suppliers with clear certifications and high credibility.


