What’s inside a Vietnamese Garment factory? Unveiling Operations
Vietnam’s textile manufacturing industry is a significant sector in the country’s economy. It is the fourth-largest exporter of textiles and garments globally, with export revenue reaching approximately $39 billion in 2020, accounting for more than 15% of the country’s total exports.
The industry has been a cornerstone of Vietnam’s rapid economic development and continues to present opportunities for foreign firms. The textile and garment industry is a driving force in Vietnam’s labor market, providing jobs for over 2.5 million people. This significant workforce underscores the industry’s pivotal role in supporting livelihoods across the country. (Data from WorldFashionExchange)
So how can a country with a textile and garment industry not as old as other developed countries still be in the top 4 of the world’s largest textile exporters? Let’s explore inside a factory in Vietnam and see how they work.
General factory infrastructure in Vietnam
General factory infrastructure in Vietnamese garment factories can vary, but here is an overview of the factory layout and organization, as well as a description of key production areas:
Garment factory layout and organization
The first thing that may strike you is the monotonous hum of thousands of sewing machines and many noises combined. The warehouse is like a thriving beehive, bustling with activity. Rows of sewing machines stretch as far as the eye can see and piles of clothes spill out into the aisles.
- Vietnamese garment factories typically have a well-organized layout to ensure efficient production processes and workflow.
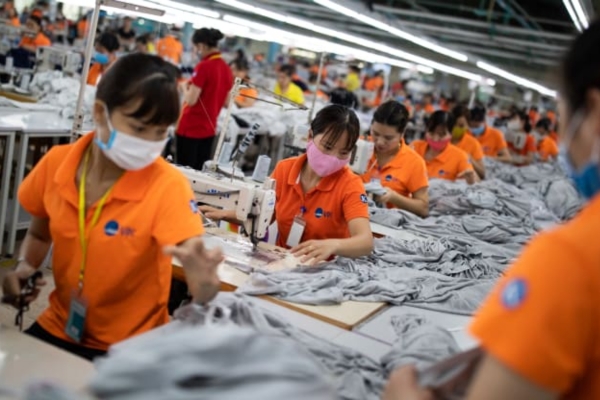

- The factory layout is designed to accommodate different production stages, from fabric cutting to sewing and finishing.
- The layout often includes designated areas for material storage, cutting rooms, sewing lines, quality control, and packaging.
- Factories may also have administrative offices, meeting rooms, and staff facilities such as restrooms and dining areas.
Key production areas
Most of all textile factories in Vietnam have at least the following 5 areas:
- Material storage: This area is used to store fabrics, trims, and other materials needed for garment production. It is important to have proper storage systems to ensure materials are well-organized and easily accessible.
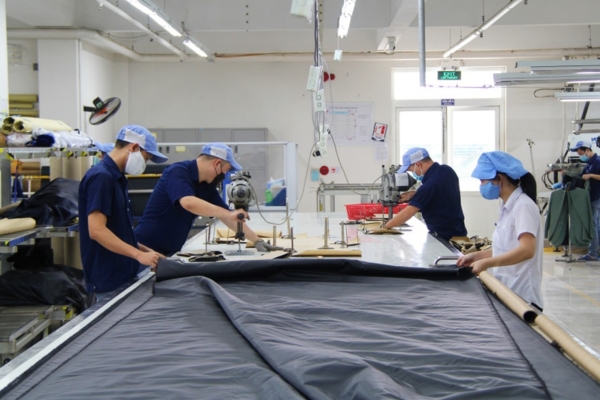
- Cutting rooms: These rooms are equipped with cutting tables, cutting machines, and tools for fabric cutting. Skilled workers measure and cut fabric according to the garment patterns.

- Sewing lines: Sewing lines are where the actual garment production takes place. Each line consists of multiple sewing machines and workers who perform specific sewing tasks, such as stitching seams, attaching buttons, or adding zippers.
- Quality control: Quality control areas are crucial for ensuring that garments meet the required standards. Inspectors check the quality of the garments at various stages of production, including fabric inspection, fitting checks, and final product inspection.
- Finishing and packaging: After the garments are sewn, they go through finishing processes such as ironing, pressing, and adding labels or tags. Once finished, the garments are packaged and prepared for shipment.
Some garment factories have a clean and tidy working environment, but many don’t and you should not be too surprised. Factories in China are much worse.
A Walk Through Production Processes
In a Vietnamese garment factory, the production processes involve several steps that transform fabric into finished products.
The workers at this textile company are very busy, so they usually don’t pay attention to visitors. So don’t be too surprised or no one will notice you, and don’t affect their work
Anh here are how things are made in the factory:
Fabric Cutting
The worker must perform many steps in this first part of production process:
- Step 1: In this area, workers will inspect incoming fabric for defects and remove or mark defective parts to maintain quality.
- Step 2: Then, workers will arrange the fabrics on the cutting table and align them to ensure uniformity in cutting.
- Step 3: Mark the positions of the pattern pieces on the fabric layers.
- Step 4: They will need to cut the fabric precisely along the marked lines and here they will use specialized tools such as rotary cutters or straight knives.
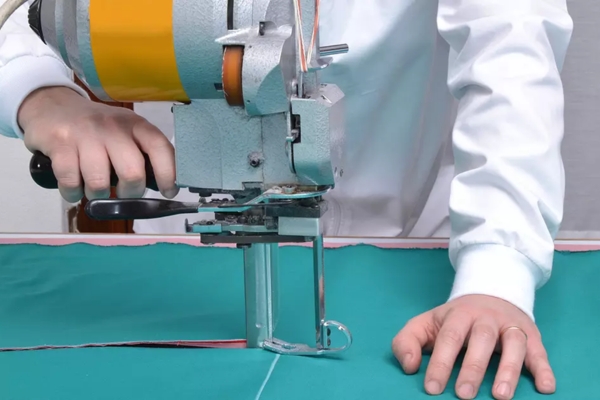

- Step 5: They will sort the cut pieces by size, style or color.
- Step 6: Textile workers will check the cut details for accuracy and defects and resolve any problems (if any) before moving on to the next stage.
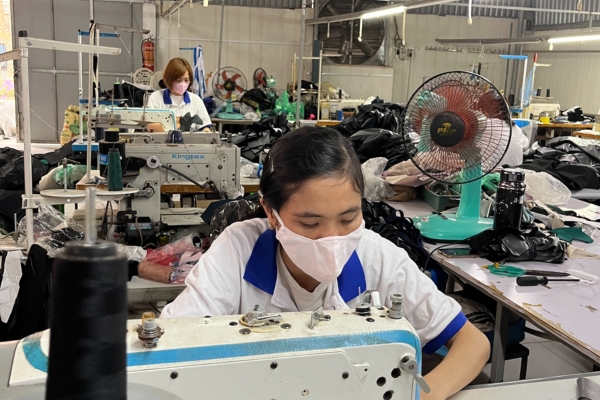
The Production Line
To make it easier to understand, the production line is the heart of the factory, where most of the production takes place.
Rows of sewing machines are operated by seamstresses, who work at a fast pace to keep up with production demands. And the clothes are assembled and sewn together as they move along the production line.

Washing and Drying
The next production stage is about forty steps away, in its own building. The washing and drying station is clean, relatively quiet and spacious. The workers here had time to relax between work hours and happily led me around the industrial machinery.
And this area also doesn’t have many tasks for workers. They will need to clean the garment to remove dirt, stains, and sizing chemicals. And it is also quite important that they need to choose the appropriate washing method based on the fabric type and clothing requirements.
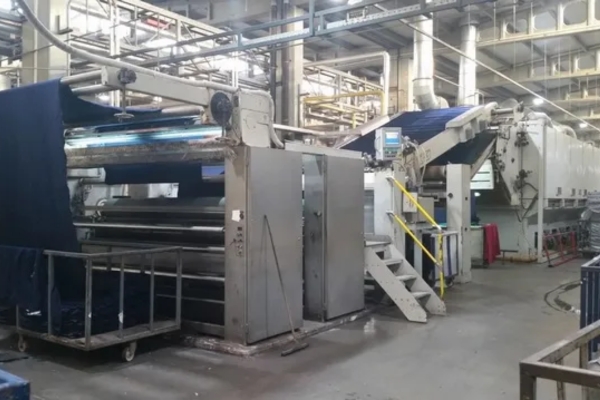

And at the drying step, workers will dry clothes using methods such as air drying or machine drying and ensure appropriate drying conditions to avoid shrinkage or damage.
Ironing, Tagging, and Packaging
Once the clothes are washed and dried, they are returned to the main warehouse for ironing, tagging and packaging.
Workers in this area are responsible for ironing out any wrinkles, attaching labels or tags containing product information, dimensions and product care instructions, and finally packaging the garment for shipping.

These steps provide a general overview of the production processes in a Vietnamese garment factory. Each step requires precision and efficiency to meet the demands of the fashion industry.
Challenges and Innovations of Vietnam Garment Factories
Vietnam’s garment industry has grown significantly and become a key industry in the global textile market. However, like any industry, it faces many challenges and requires innovation to truly stand out from other strong exporting countries.
Common challenges faced by Vietnamese factories
There are 5 common challenges that many Vietnamese factories have to face nowadays:
1. Declining orders: Vietnamese garment factories have been experiencing lower than expected orders from key trading partners, leading to financial difficulties and layoffs.
2. External factors: Rising inflation in developed markets, such as the Western Hemisphere, has impacted consumer spending and reduced demand for textiles and garments.
3. Labor shortage: Despite having a large labor force, the industry is facing a huge shortage of skilled workers. This shortage hampers productivity and limits the industry’s ability to meet market demands.
4. Increasing labor costs: As the industry grows and wages rise, labor costs have been increasing, affecting the competitiveness of Vietnamese garment factories.
5. Uncertain financial status: The depreciation of the Vietnamese dong against the US dollar and high shipping costs due to ongoing tensions in the Red Sea have increased costs for exporters and importers.
Innovative solutions and technologies
Yet, everything has its solution. Vietnamese factories can pay attention to the following innovative methods and technologies to increase competitiveness
- Technology adoption: Vietnamese garment factories are embracing Industry 4.0 principles and undergoing digital transformations. They are implementing end-to-end integrated solutions such as Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) to optimize processes and boost efficiency.
However, this is still a problem as some garment factories can’t afford to apply these modern technologies into their production
- Robotics and automation: To reduce labor-intensive tasks and improve precision, Vietnamese garment factories are incorporating robotics and automation solutions on the factory floor. These technologies help reduce production costs and enhance competitiveness.
- Skilled labor development: To address the shortage of skilled labor, the industry is investing in vocational training programs and collaborating with universities and research institutes. These initiatives aim to provide the industry with a skilled workforce that meets the evolving market demands.
- Research and Development (R&D): Vietnamese garment factories should focus on enhancing design capabilities and increasing research and development of products rather than remaining “loyal” to a particular style – you wouldn’t want to repeat Nokia’s mistake. And they will need to meet customer demand for high quality, unique design, and sustainable products.
And if you want an example of a factory that has been applying these innovative measures and is the leading factory in Vietnam producing smocking clothing products for children, I would say it is K-Embroidery.

K-Embroidery is a factory specializing in exporting children’s smocking clothing products to foreign partners like the US, UK, Japan, …, so modern technologies and advanced textile methods are always updated by K-Embroidery, reviewed and applied to the production process.
In addition, K-Embroidery uses a combination of hand and machine sewing to ensure a fast production process while maintaining high product quality, satisfying the most demanding customers in the world.
And that’s not all, K-Embroidery always has a very professional R&D team and management board, they will research and find new methods to improve products and production processes.
Conclusion
The above article has been shared with readers about what happens inside a textile factory in Vietnam. If you have any questions or suggestions about the content, please leave a comment below! K-Embroidery is always welcome and love to receive feedback from you!


